
Greek Fire
Byzantine naval troops deploy Greek Fire in the 1100s against the forces of Thomas the Slav. Madrid Stylitzes, Biblioteca Nacional de España

Trebuchet hurls fire pot
A trebuchet of the 1200s equipped with defensive stockades hurls a fire pot over a castle wall. Harper's Magazine
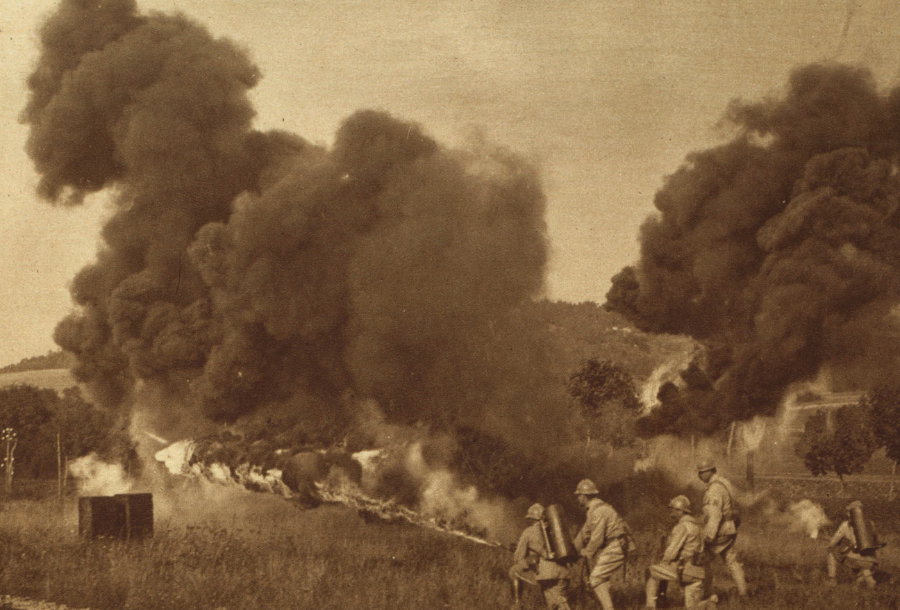

World War I
Troops on the Western Front use flamethrowers to attack enemies in the forest to the left. New York Times/Library of Congress
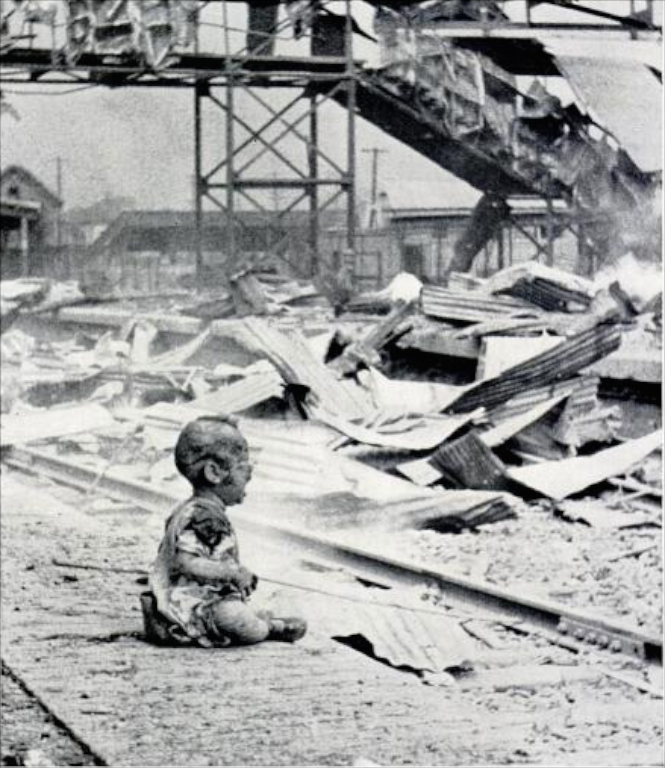

1937 Shanghai
A baby cries at Shanghai's South Station on August 28, 1937 after a Japanese incendiary bomb attack. Office of War Information/National Archives

1941 Coventry Cathedral
Prime Minister Winston Churchill visits the ruins of Coventry Cathedral in September 1941, destroyed by incendiary bombardments in November 1940. Imperial War Museum/Library of Congress
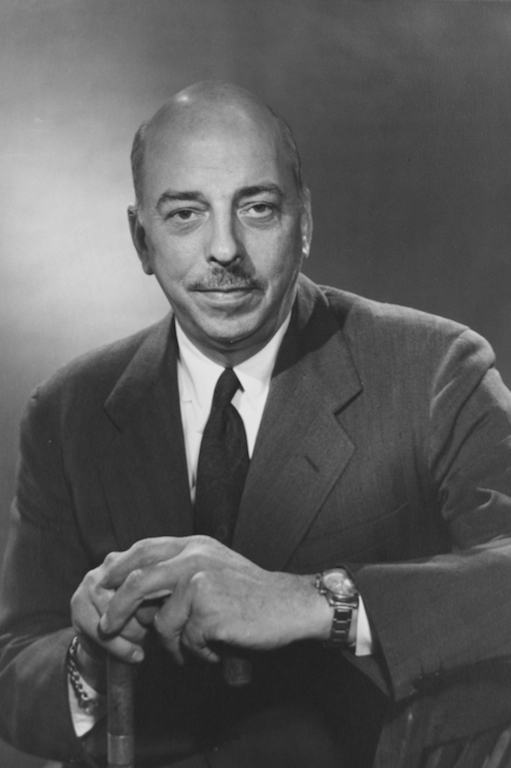

Professor Louis Fieser, father of napalm
Harvard University’s Sheldon Emery Professor of Organic Chemistry Louis Fieser, father of napalm. Harvard University Archives

1942 M-47 bombshell
Mustard gas bombshell supplied to Harvard University researchers by the War Department for the first tests of napalm bombs. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 Harvard College meat grinder mixes napalm
A Harvard College dining hall meat grinder slices napalm into strands before it is mixed with gasoline and siphoned to an M-47 bombshell, originally designed for mustard gas. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method.

1942 Demonstration of mixing napalm
Person believed to be Louis Fieser demonstrates how to prepare napalm from napalm powder to the right and gasoline to the left. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 Just the right gel
Person believed to be Louis Fieser demonstrates how effectively formulated napalm gel is not too loose and not too firm: just right. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 Harvard University test pond with napalm bomb
A napalm bomb stands in a test pond on the Harvard College soccer field, behind the Business School, before its first trial on Independence Day July 4. Tennis players in whites are in the background. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 First field test of a napalm bomb
First field test of a napalm bomb, Harvard University: July 4, 1942. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 Review of napalm bomb test results
Assistants extinguish gobs of burning napalm and collect samples approximately one minute after detonation of napalm bomb (note empty tennis courts). Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1942 White phosphorus igniter test at Harvard University
White phosphorus produces a smokescreen intended to hamper firefighters if used in combat. Harvard's football stadium is visible in the background. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

2008 Harvard College soccer field
A contemporary view of the Harvard College soccer field. Tennis courts are in the background (the building in front of Business School library tower was built after 1942). Robert Neer

1943 Plan for a German-style house for napalm test
Standard Oil’s plan for a Central German-style house used for napalm bomb tests. Focus is on the bedroom and attic. Comments note the performance of various incendiary bomb designs. National Defense Research Committee

1943 German-style bedroom for napalm tests
A German-style bedroom furnished for napalm and other incendiary bomb tests by the Factory Mutual Research Corporation. Image on top shows the view from the door; on the bottom is the view from the window. National Defense Research Committee

1943 Standard Oil napalm burning test
Flames pour from the second-story window of a test structure as spectators observe an incendiary bomb test by Standard Oil Development Company researchers. National Defense Research Committee

1943 German and Japanese residences for napalm bomb tests
Views of German and Japanese residences in incendiary bomb test villages at Dugway Proving Grounds, Utah. National Defense Research Committee

1943? Standard Oil napalm tests
Time lapse photographs of Standard Oil Development Company napalm house burning test. National Defense Research Committee

1943? Standard Oil test home burns
Home ignited by napalm burns during a Standard Oil Development Company incendiary weapons test. National Defense Research Committee

1944 Japanese room for napalm tests
A Japanese room built for incendiary bomb tests at Edgewood Arsenal, Maryland. Furnishings include tatami mats, shoji screens, a low table with cushions, a storage chest, and bedding. National Defense Research Committee
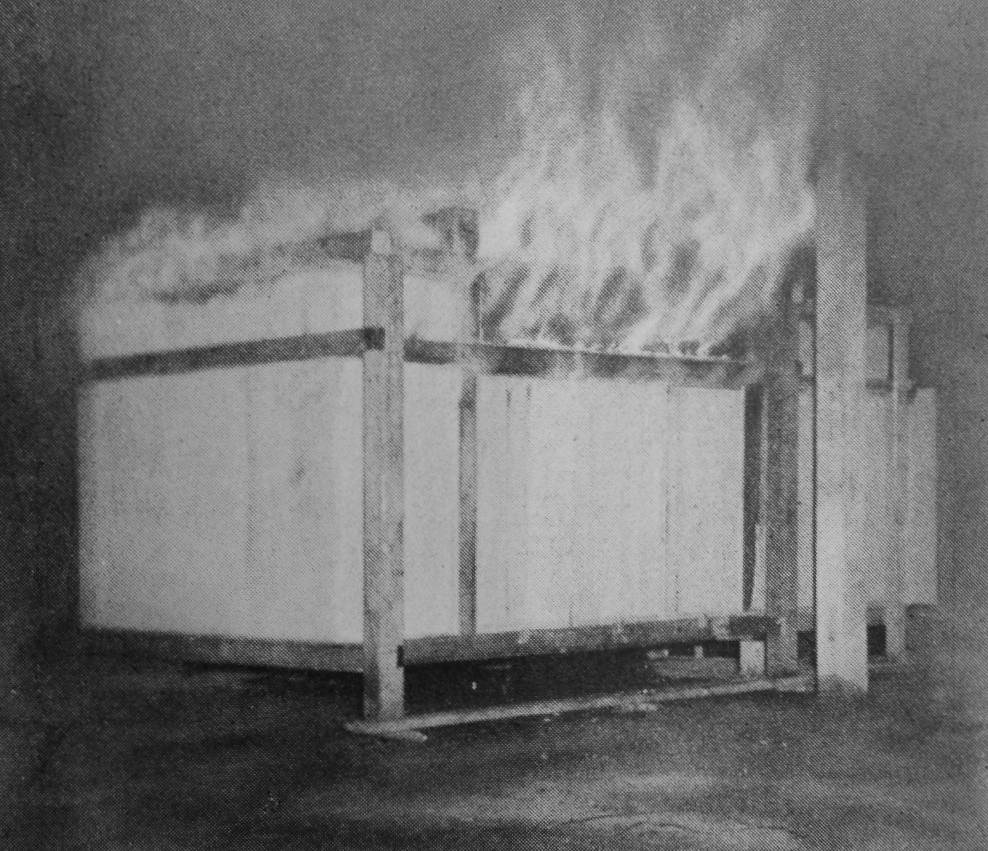

1944 Japanese test room successfully ignited
Japanese room at Edgewood Arsenal, Maryland burns after ignition with napalm. National Defense Research Committee

1943? Louis Fieser at Carlsbad Army Air Base
Prof. Louis Fieser at Carlsbad Army Air Base during bat bomb project tests. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

Mexican Free-Tailed Bat
Mexican Free-Tailed Bat (todaria mexicano) used by U.S. Marine Corps for Project X-Ray napalm bat bomb program. Louis Fieser, The Scientific Method

1943 Bat with napalm time bomb
A ten- to eleven-gram Mexican free-tailed bat carries a 17.5 gram napalm time bomb designed by Louis Fieser and intended for attacks on Japan. Later bomb models were smaller (German translation for the weapon: Kamikazefledermäuse mit Napalmbehältern). Harvard University Archives

1945 Napalm flamethrower
U.S. M1A1 flamethrower demonstrates increased range possible with napalm fuel. National Defense Research Committee.

1945 U.S. flame tank on Okinawa
Medium U.S. tank with flame thrower firing on Japanese defenders on Okinawa. U.S. Army

1943? M-69 napalm firebombs
1943? Sectional models of AN-M-69 and M-69-WP bombs showing stabilizing streamers, sock filled with napalm, optional white phosphorus charge to create smokescreen and impair firefighting, and time-delay fuze. Each bomb weighed 6.2 pounds and contained 2.6 pounds of napalm. In total, America dropped over 40,000 tons of M-69 bombs on Japan: 80 million pounds of bombs, 12.9 million individual shells, and 33.5 million pounds of napalm. Standard Oil Development Company

1943? Napalm cluster bomb
1943? E6R2 aimable cluster for the M-69 bomb. Each cluster weighed 425 pounds and contained 38 individual bombs. Standard Oil Development Company

1945 B-29 with napalm cluster bombs
A B-29 with clusters of napalm bombs waiting to be loaded. National Defense Research Committee

1945 Tokyo after napalm attack
Nihonbashi District in Tokyo after March 9 napalm attack. Note the complete destruction of the Japanese type buildings, and the gutted shells of the concrete structures. Life magazine/National Defense Research Committee

1945 Casualties in Tokyo
Bodies fill the Sumida River after the 9 March 1945 napalm attack.

1945 Tokyo firestorm victims
Victims of 1945 U.S. incendiary bomb attacks on Tokyo. Wikipedia

1945 Burned-out areas of Tokyo
Map shows areas of Tokyo destroyed in 1945 napalm firebomb attacks. U.S. Army

1945 U.S. firebombing "LeMay warning leaflet"
Leaflets dropped over 35 Japanese cities on 1 August show the names of 12 cities targeted for incineration: "Read this carefully as it may save your life or the life of a relative or friend. In the next few days, some or all of the cities named on the reverse side will be destroyed by American bombs …." U.S. Army/Wikipedia

1945 Osaka destroyed
Destruction from napalm attacks on Osaka was comparable to that of Tokyo and Hiroshima. U.S. Army

1945 Toyama destroyed
Night napalm bomb attack on Toyama. U.S. Army

1945 Hiroshima destroyed
Destruction after the atomic bomb attack on Hiroshima was comparable to that wrought by the firebomb strikes on Tokyo, Osaka and other major Japanese cities.
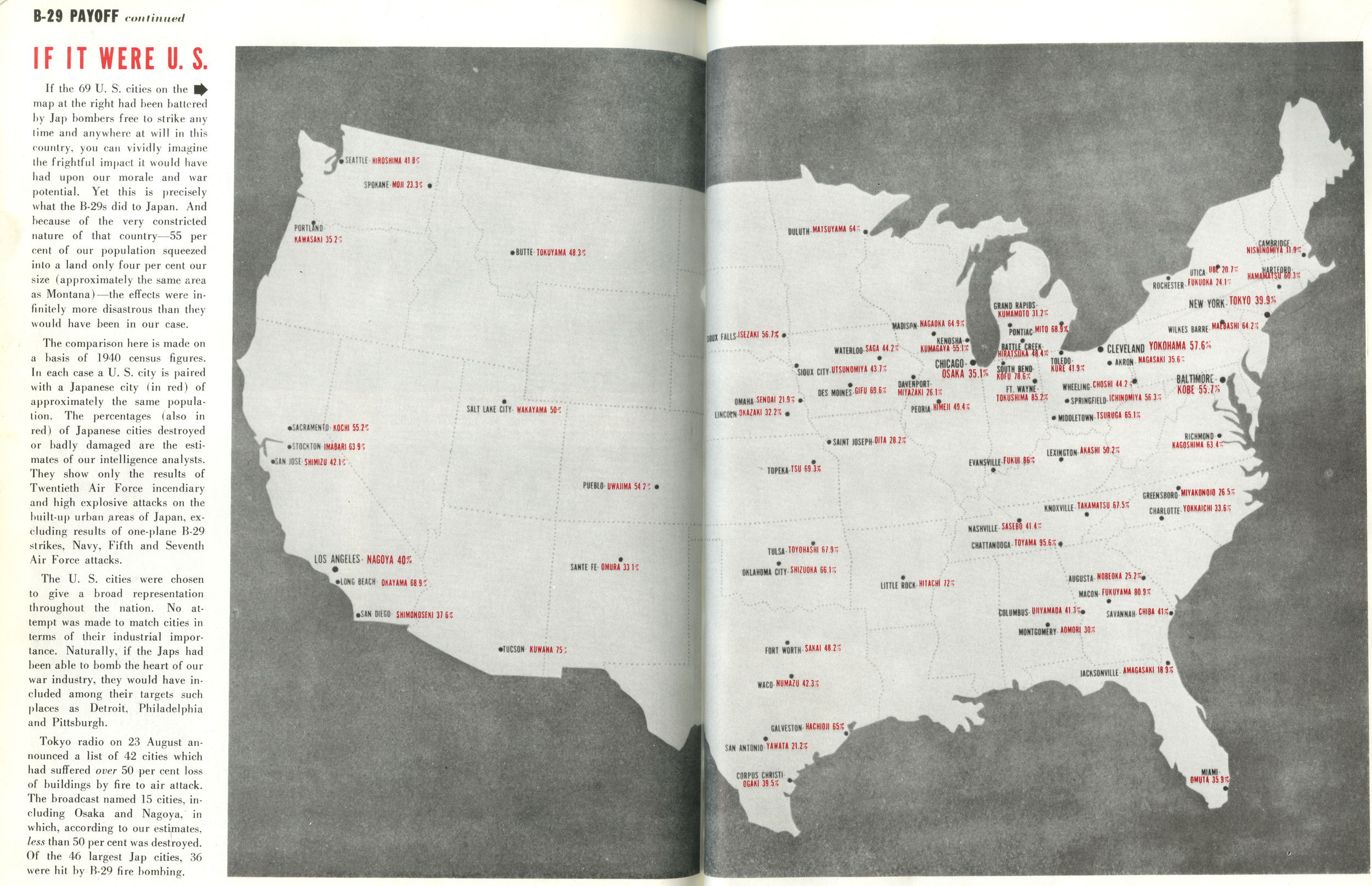
1945 Japanese cities destroyed mapped to US
A U.S. Army map showing Japanese cities destroyed compared to U.S. cities. U.S. Army

1950-1953 Korean war napalm strike
A napalm bomb explodes on a factory in Korea. John Halliday and Bruce Cumings. Korea: The Unknown War. 1988: Viking/U.S. Army

1952 U.S. Korean War warning map
Map dropped by U.S. airplanes shows railroads and highways to be bombed. Austin Stevens. “U. S. Counters Red Charges Napalm Is Used on Civilians; U. N. Leaflets Warning North Koreans of Bombing U. S. COUNTERS REDS ON NAPALM BOMBS.” 19 August 1952. NYTimes.com.

1951 Korean civilians burned by napalm
A trio of South Korean women, burned by U.S. napalm bombs, at an aid station near Suwon, South Korea on 4 February 1951. Associated Press/National Archives

1950-1953 Pyongyang after napalm bombing
Pyongyang after United Nations attacks with napalm and explosives. Vitali S. Latov/John Halliday and Bruce Cumings. Korea: The Unknown War. 1988: Viking.

1967 U.S.S. Liberty damaged by napalm and explosives
Damage to U.S. intelligence vessel U.S.S. Liberty's starboard hull and superstructure after mistaken Israeli attack with napalm and explosives. U.S. Navy/Wikipedia

U.S.S. Liberty damaged by napalm and explosives
Damage to U.S. intelligence vessel U.S.S. Liberty from mistaken Israeli attack with napalm and explosives. U.S. Navy/Wikipedia

1967 Ramparts image of a burned Vietnamese child
A photograph of a Vietnamese child burned by napalm, published in January 1967 by Ramparts magazine: one of the first images widely distributed in the U.S. of a civilian casualty from the incendiary gel. William F. Pepper/Ramparts

1967 Vietnamese child burned by napalm
Another photograph of a Vietnamese child injured by napalm from the January 1967 issue of Ramparts magazine. William F. Pepper/Ramparts

1967 University of Wisconsin-Madison anti-napalm protest
Demonstration against napalm manufacturer Dow Chemical Corporation and U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Wisconsin Historical Association

1967 UWI-Madison "Dow Riot"
View of the anti-Dow Chemical campus protest seen from a broken window in the Commerce Building of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Wisconsin Historical Association

1967 UWI-Madison anti-napalm protest
Poster with a large image of the October 1967 "Dow Riot" on the University of Wisconsin-Madison campus showing riot police beating protesters. Includes the Lyndon Baines Johnson quote, "Our foreign policy must always be an extension of this nation's domestic policy. Our safest guide to what we do abroad is a good look at what we are doing at home." Wisconsin Historical Association

1993 U.S. Navy MK-77 napalm firebomb
Navy technicians load an MK-77 napalm firebomb on an F/A-18 Hornet aircraft at the Naval Air Warfare Center target complex at Fallon Naval Air Station, Nevada. U.S. Navy/Wikipedia

1999 Oregon Navy burns grounded freighter with napalm
U.S. Navy napalm and explosives create a giant fireball over the grounded freighter New Carissa near Coos Bay, Oregon. Brandon Brewer/U.S. Coast Guard Digital

2007 Napalm Topical Fat Loss Matrix
Skin cream marketed by Avant Research. Caleb Stone/Avant Labs/Robert Neer

1998 Napalm bombs in storage at Fallbrook Naval Weapons Station, California
About 23 million pounds of Vietnam War-era napalm bombs cover 67 acres at Fallbrook Naval Weapons Station, between Los Angeles and San Diego, in 1998. Jamie Scott Lytle/Sygma/Corbis






















































